What is the Religion of Islam? Unveiling World’s 2nd Largest Religion

Islam is a religion that focuses on submitting to God, known as Allah. It’s the second-largest religion globally, with over 1.8 billion followers. Islam shares similarities with Judaism and Christianity as an Abrahamic faith. Let’s explore its beliefs, practices, and history in more detail.
What is the Religion of Islam?
Islam is a monotheistic religion, meaning followers believe in one God, known as Allah in Arabic. The word Islam itself means “submission” in Arabic, referring to the idea of submitting to God’s will.
Unlike Christianity, Islam rejects the concept of the Trinity, emphasizing the oneness of God. Prophets such as Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and Muhammad are considered messengers of God, with Muhammad being the final prophet who brought the ultimate revelation.
Here are some key aspects of Islam:
The Quran

Imagine a book containing God’s direct words, a guide for every aspect of life. That’s the Quran for Muslims. It’s considered the most important source of Islamic teachings, covering everything from religious duties and social conduct to morality and ethics. Muslims hold the Quran in such high esteem that they treat it with utmost respect, often memorizing passages and reciting them in prayers.
Five Pillars of Islam
Five core practices, known as the Five Pillars of Islam, act as the foundation for a Muslim’s daily life. These pillars are like five strong pillars holding up a building – essential for a strong and fulfilling Islamic life.
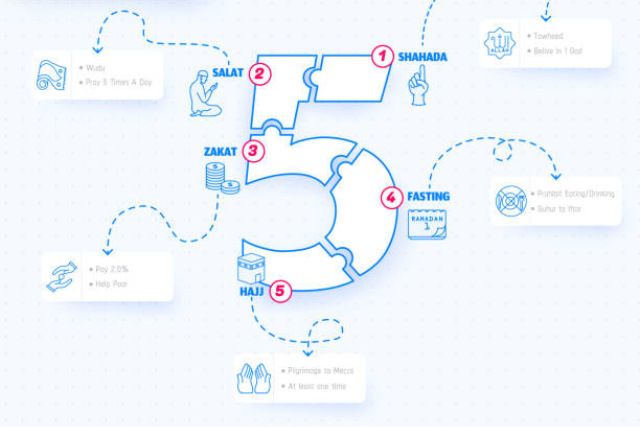
- Shahada (Declaration of Faith): This is the fundamental belief, a simple yet powerful statement: “There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah.” It’s the foundation upon which everything else rests, a declaration of complete devotion to God and acceptance of Muhammad as his messenger.
- Salat (Prayer): Muslims perform five daily prayers at specific times throughout the day. These prayers involve specific postures, like standing, bowing, and prostrating. Imagine these prayers as regular conversations with Allah, expressing gratitude, seeking forgiveness, and connecting with the divine.
- Zakat (Charity): Sharing your wealth with those less fortunate is a vital concept in Islam. Zakat is a mandatory charitable contribution that purifies one’s wealth and helps those in need. It teaches generosity, compassion, and the importance of social responsibility.
- Sawm (Fasting): During the holy month of Ramadan, Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other sensual activities from dawn to dusk. This practice fosters self-discipline, empathy for the less fortunate, and spiritual growth. Imagine fasting as a way to cleanse the body and soul, reminding Muslims of their dependence on God and the struggles of those less fortunate.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage): Once in a lifetime, if physically and financially able, Muslims are expected to undertake a pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest city in Islam. This pilgrimage involves a series of rituals that commemorate the Prophet Abraham’s devotion to God. It’s a powerful experience that brings Muslims from all walks of life together in a shared act of faith.
Sharia Law
Imagine a compass guiding you on your journey. Sharia law serves a similar purpose in Islam. It’s a moral and legal code derived from the Quran and the teachings of Prophet Muhammad, offering guidance on various aspects of life, including family matters, business dealings, and criminal justice. Think of it as a framework for living a life according to Islamic principles. However, it’s important to understand that the interpretation and implementation of Sharia law can vary depending on different schools of thought within Islam.
Sunni and Shi’a
Just like a mighty tree can have different branches, Islam has two major denominations: Sunni and Shi’a. Sunnis, forming the majority, believe the rightful successors to Prophet Muhammad were the first four Caliphs (leaders) of the Islamic community.

Shi’a Muslims, on the other hand, believe that only descendants of Prophet Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, Ali, are the legitimate leaders. These contrasting views on leadership led to a historical split within Islam. However, both Sunni and Shi’a Muslims share the core beliefs of Islam and hold the Quran and the teachings of Prophet Muhammad in high regard.
Islam in the Modern World
Unfortunately, misconceptions and stereotypes often cloud our understanding of Islam. Terrorism and violence do not represent the core values of Islam, which emphasizes peace, justice, and compassion.
Muslims come from all walks of life, contributing significantly to various fields across the globe. They are doctors, engineers, artists, teachers, and everyday people enriching societies with their cultural heritage and traditions. Imagine a vibrant tapestry woven with countless threads – that’s the beauty of Islam in the modern world.
The Future of Islam
Like any religion, Islam faces challenges in the modern world. Issues like balancing tradition with modernity, navigating social and political changes, and promoting interfaith dialogue are ongoing conversations within Muslim communities.
However, Islam emphasizes peace, justice, and compassion, and Muslims from diverse backgrounds contribute significantly to various fields globally. Countries like Turkey, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia play significant roles in shaping Islamic culture, history, and religious practices.
FAQs
What is Islam vs Christianity?
Both Islam and Christianity are Abrahamic religions, which means they trace their roots back to the prophet Abraham. They share many beliefs, like believing in one God and the importance of prophets. However, there are also key differences. Muslims believe Muhammad was the final prophet, while Christians believe Jesus was the Son of God. The holy book of Islam is the Quran, while Christians follow the Bible.
What is the holy religion of Islam?
Islam itself is considered the holy religion for Muslims. The word “Islam” means “submission” to God (Allah).
What is the true religion of Islam?
The concept of “true religion” is subjective and varies across faiths. Muslims believe Islam is the complete and final revelation from God, following a long line of prophets.
Do Islam believe in Jesus?
Yes, Muslims believe in Jesus (referred to as Isa in Arabic) as an important prophet sent by God. They respect him but don’t consider him the Son of God as in Christianity.
What Bible do Muslims use?
Muslims revere the Torah (received by Moses) and the Gospel (teachings of Jesus) but believe these scriptures have been corrupted or incomplete over time. Their holy book is the Quran, believed to be the final revelation from God.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Islam is a monotheistic religion centered around the concept of submitting to God’s will, known as Allah. Muslims believe in a long line of prophets, including Jesus (referred to as Isa), culminating in Prophet Muhammad as the final messenger. The Quran, believed to be the direct word of God revealed to Prophet Muhammad, serves as the foundation of Islamic faith and practice.
So, to answer the question “what is the religion of Islam?” It’s a religion built on devotion to one God, following the guidance in the Quran and teachings of Prophet Muhammad. Understanding Islam’s core beliefs and practices fosters greater respect and appreciation for this rich and vibrant faith tradition.





